The Symposium of Student Research, Scholarship, and Creative Activities is a salute to the scholarly explorations of an incredible variety of Wright State's undergraduate and graduate students.
Open to all disciplines, this daylong event showcases lectures, posters, videos, slideshows, and other presentations of research, scholarship, and creative activities produced during the year.
-

Understanding Physiological Responses for Intelligent Posture Detection Using Wearable Technology
Chaitanya Vardhini Anumula, Tanvi Banerjee, and Anuradha Oak
This study investigates the physiological impact of Iyengar yoga at the pose-level using EmbracePlus wearable smartwatch, for data recording and personalized yoga pose detection for tracking.
-

Peer Supporter Perspectives on the Roots of Addiction:A Qualitative Study
Elise Hubert and Sydney Silverstein
The aim of this study is to qualitatively evaluate the origins of addiction through the perspective of individuals with lived experience.
-

Furosemide for Postpartum Management of Hypertensive Disorders: A Randomized Controlled Study
Margaret J. Herr, Holly M. Johnson, Rose A. Maxwell, Zachary Candela, and Sheela Barhan
Loop diuretics have been investigated for managing postpartum hypertensive disorders, but there is currently insufficient clinical evidence pointing to any single agent. This study aims to compare blood pressure (BP) outcomes for patients with gestational hypertensive disorders receiving labetalol alone versus labetalol + furosemide during postpartum hospital stay. The primary aim was to learn if loop diuretic incorporation in conjunction with labetalol could lower the need for additional anti-hypertensive agents.
-

Academic Success 101: Strategies for Promoting a Resilient Self-Concept in Women Doctoral Students
Gabrielle Armer, LaTrelle D. Jackson, and Susan George
Although female graduate psychology students outnumber male students three to one (Fowler, et. al., 2018), women are still likely to experience more challenges than men during their doctoral programs (Bireda, 2015). Women doctoral students are faced with the challenges of learning how to integrate their personal identities such as partner, mother, or caregiver with their emerging identity of academician (Rockinson-Szapkiw et al., 2017). Women doctoral students often describe these conflicting roles as altering their overall self-concept, which often leads to feelings of loss, mistrust, and disconnect (Balatti & Whitehouse, 2001). This poster highlights ways in which self-concept in women may impact academic success. Recommendations are provided that support the cultivation of self-concept resilience factors and promote the academic success of women doctoral students.
-
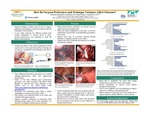
How Do Surgeon Preferences and Technique Variances Affect Outcome?
Anastasia Axiopoulou, Caroline G. L. Cao, Katherine Lin MD, and Keith Watson MD
The goal of the research project is to create a blue-print of a robot-assisted hysterectomy procedure to support design and evaluation of technology to enhance system performance. To create this blue-print, we will conduct a task analysis, model the cognitive task flow and decision making, and develop a simulation of the hysterectomy procedure. The surgical simulation will be used as a platform to train surgeons on robotic-assisted hysterectomies, as well as to assess learning and performance. Additionally, it will be used to design and develop techniques and novel technology to support surgeons in their performance of the surgery. Current research efforts are focused on the task analysis step. Data collection included observations in the hospital operating room, interviews with surgeons and nurses, analysis of surgery instructional videos and textbooks. A hierarchical task decomposition has been conducted. Thus far, results of the task analysis reveal several different types of hysterectomies and large variance in surgical techniques based on each surgeon’s preference. These findings will be validated by expert surgeons, and supplemented with a cognitive task analysis. In the next phase of the research project, we will identify several critical decision points within the surgical procedure that include variations in the use of surgical tools or variations in the sequence of actions. For example, the use of a uterine manipulator during the hysterectomy procedure seems to have an impact on the surgeon’s ease, speed, and accuracy while performing the procedure. These variations will be modeled and incorporated into the surgical simulation during development. Ultimately, the simulator will be used to train and assess the physician’s performance. It will also allow us to analyze the difference in techniques and how that affects patient outcome. A surgical simulation that has been designed and developed based on a systematic task analysis and cognitive model will allow us to more accurately study the requirements and constraints of the surgical environment, and support future innovate to enhance surgical performance and patient safety.
-
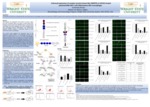
Enhanced expression of receptor tyrosine kinase Mer (MERTK) on SOCS3-treated polarized RAW 264.7 anti-inflammatory M2c macrophages
Sankhadip Bhadra
Macrophages are phagocytic cells located in tissues, organs and even circulated within our body as white blood cells. Based on the local cytokine milieu in tissue sites, macrophages may be polarized into pro-inflammatory M1 or anti-inflammatory M2 phenotypes. Receptor tyrosine kinase Mer (MERTK) helps in clearing dead neutrophils and other apoptotic cells from damaged tissue sites preventing chronic inflammation and autoimmune disorders. MERTK aids in the maintenance of tissue homeostasis and wound healing. Phosphatidylserine (PtdSer) present on the surface of apoptotic cells release “eat me” signals which are recognized by the two “bridging ligands” of MERTK receptor, Gas6 and ProS. The binding of the ligands to PtdSer initiates intracellular signals leading to phagocytosis of the cell. MERTK receptor is expressed mostly on M2c macrophages.
The current study explores the expression rate of the phagocytic receptor MERTK, on macrophages polarized with either IL-10 (M2c ells) or IL-4 or IL-13 (M2a macrophages) following treatment with the suppressor of cytokine signaling SOCS3 in comparison with macrophage polarization with only IL-10 or IL-4 or IL-13 . It exhibits an enhancement in the expression of the phagocytic MERTK receptor on the surface of IL-10 polarized M2c macrophage when treated with SOCS3 in comparison to IL-10 polarized M2c macrophage, IL-4 polarized M2a macrophage and IL-13 treated M2a macrophage. IL-13 polarized M2a macrophage also shows an increase in the expression of MERTK receptor which is similar to a previous study where a similar receptor to MERTK termed “Axl receptor” is enhanced by IL-13 treatment on bone- marrow derived macrophage. SOCS3 treated with IL-13 polarized M2a macrophage acts as a negative regulator of MERTK receptor by decreasing the expression contrasting to the effect of SOCS3 on IL-10 which enhances the expression.
Future research will involve co-culturing SOCS3 polarized M2 macrophages with apoptotic cells such as N2a neuroblastoma cells.
-

Relief of Procedural Pain in Infants and Neonates
Allye Camden
Procedural pain occurs in the hospital setting due to a variety of procedures and treatments conducted throughout a patient’s stay. Pain is often assessed in infants and neonates but is not always treated consistently due to the multiple number of pain relief methods. The objective of this literature review is to identify the most effective interventions to relieve procedural pain in infants and neonates. Forty articles were analyzed and synthesized to determine the best pain relief methods to use when providing nursing care to infants and neonates. Based on the results of the literature review, nutritive sucking, positioning techniques, and combined interventions are recommended as first-line pain relief methods for infants and neonates. However, further research is needed to compare the effectiveness of these different methods.
-

The Relationship Between Object-Based Judgments and Judgments of Relative Direction as Measures of Spatial Memory
Zachary Carpenter, Tressa Molinar, and Herbert A. Colle
There are frequently two different conceptions used to describe what people store in their memory for environmental layouts. The SOLAR (Straight-Line Object-Based, Local Angular Relations) model and the quasi-Euclidean Framework model. The Framework model assumes that people store coordinated points in their layout of spatial memory. This grid-like representation of points is then used to remember layouts. A common, natural judgment that is used within the Framework model are called judgments of relative direction (JRDs). The SOLAR model, on the other hand, assumes people remember and store information about 3D objects, so characteristics such as fronts can be used as a surface referent to create a third source of information. The SOLAR model assumes that objects are related via straight-line angular relations, so object-based judgments (OBJs) are used within the SOLAR model. Navigation paths also play a key role in the formation of spatial memory. So, the current research examines the relationship between JRDs and OBJs by creating natural, navigable environments. The angles between the facing objects were crafted in a way that certain queries had the same angular relationship across rooms, which allowed for the direct comparison between the two measurements. If OBJs and JRDs use the same underlying processes, the two measurements should be related and should be able to be used to predict each other. This is exactly what our results suggest. This is an important finding because using alternative measures will shed light on spatial memory processes.
-
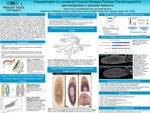
Characterization of a Conserved Transient Receptor Potential Channel Required for Spermatogenesis in Planarian Flatworms
Haley Curry and Labib Rouhana
The molecular processes underlying the control of external stimuli on development of the reproductive system remain to be understood. The Transient Receptor Potential superfamily of proteins (TRPs) consists of cation channels that respond to external stimuli and are abundant in the somatosensory as well as reproductive systems. Mammalian TRP-Melastatin 3 (TRPM3) channels are activated by heat and the neurosteroid pregnenolone. Here we characterize an ortholog of TRPM3 in the planarian flatworm Schmidtea mediterranea (Smed-TRPM3). Smed-TRPM3 was hypothesized to play a role in germline development due to enriched expression in the reproductive system of sexual planarians. In situ hybridization analysis revealed that Smed-TRPM3 is preferentially expressed in planarian testes and ovaries. Functional analysis by RNA interference (RNAi) revealed that Smed-TRPM3 promotes spermatogenesis, as sexual Smed-TRPM3(RNAi) planarians had fewer and less-developed testes compared to control knockdowns. Asexual Smed-TRPM3(RNAi) animals had fewer nanos+ clusters compared to controls which may indicate that the observed spermatogenesis defects are due to the loss of male germline stem cells. We hypothesize that Smed-TRPM3 responds to the hormone pregnenolone to ultimately regulate gonad development. Alternatively, Smed-TRPM3 may be regulating reproductive development in response to temperature.
-

Defect Characterization of Additively Manufactured Parts
Sabrina D'Alesandro, Joy Gockel, and Andrew Harvey
This document describes various image processing techniques to be used for defect characterization of additively manufactured parts. This will help the reader gain knowledge of materials science engineering and the nuances in analyzing data from image processing software.
Additive manufacturing is shaping the manufacturing world through simplistic household printers’ to more complex metal printers used for a variety of applications. Specifically, laser powder bed fusion (LPBF) is an additive manufacturing process that deposits metal powder over the build plate and melts it with a laser in the shape of the build part. In order to make LPBF more efficient with higher quality material, an experiment was done using in-situ monitoring sensors to observe the LPBF process as it prints the nickel super-alloy 718. The focus of this experiment was to observe defects in the printing process such as pores and inclusions. The LPBF machine printed two separate parts, one small coupon and one larger coupon. Changing the geometry for LPBF parts will create different outcomes microscopically, because of the different thermal histories, that result in different defect characteristics. Using image processing techniques, the defects can be characterized to help understand the relationship between geometry and porosity. The implications of this research highlight the impact to the structural integrity of printed LPBF parts, which will help ensure that future materials have less defects, are stronger, and have a higher level of quality.
-

Measuring Nomophobia and Exploration of Consequences and Comorbidities
Sarah Marie Fryman and William L. Romine
Excessive use of smartphones has coined the term “Nomophobia”, or fear of not being able to use your smartphone. For many, these devices have become an extension of ourselves, which raises hesitation on whether or not society has become addicted to smartphones. Specific diagnostic criteria for smartphone addiction have yet to be settled, and even appropriate to use the word “addiction” when describing excessive usage of smartphones is controversial.
We therefore explore utilize current measures to explore the symptoms of nomophobia and their hierarchy, as well as comorbidities including social anxiety, self-esteem, distracted driving and sleep quality. A total of 176 adults from a research-intensive university in the Midwestern United States completed an anonymous online survey. Through factor analytic and Rasch methods, it was found that based on a single measure for one’s level of nomophobia, the degree to which mobile phone use interferes with daily life can be qualified. The relationship between nomophobia and social anxiety supports the hypothesis that mobile phone addiction can be magnified by personality traits and other psychiatric comorbidities. It is apparent that technology addiction and cell phone addiction need to be studied among a greater population, especially among women and those with social anxiety.
-

TIP60 regulation of ΔNp63α is Associated with Cisplatin Resistance
Akshay Hira, Andrew Stacy, Jin Zhang, Michael P. Craig, and Madhavi Kadakia
About 5.4 million basal and squamous cell skin cancers are diagnosed every year in the US. ΔNp63a, a member of the p53 transcription factor family, is overexpressed in non-melanoma skin cancer and regulates cell survival, migration and invasion. TIP60 is histone acetyltransferase (HAT) which mediates cellular processes such as transcription and the DNA damage response (DDR). Previous studies in our lab have shown that overexpression of TIP60 induces ΔNp63a protein stabilization in a catalytic-dependent manner. Since ΔNp63a is known to transcriptionally regulate several DDR genes and promote cisplatin resistance, its stabilization by TIP60 may contribute to the failure of platinum-based drugs in squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). We hypothesize that TIP60 regulates the transcriptional activity of ΔNp63a thereby modulating chemoresistance. In this study, we showed that overexpression of TIP60 in both H1299 and A431 cells led to stabilization of ΔNp63α, while TIP60 silencing in A431 cell lines led to a decrease in endogenous ΔNp63α transcript and protein levels, thus confirming that TIP60 positively regulates ΔNp63α in these cell lines. Increased levels of ΔNp63a TIP60 correlated with increased ΔNp63a expression and contributed to cisplatin resistance. Further, stable expression of TIP60 or ΔNp63α individually promoted resistance to cisplatin and reduced cell death, whereas loss of ΔNp63α and TIP60 sensitized cells to cisplatin. Higher acetylation of ΔNp63a and TIP60 were seen cisplatin resistant cells. Taken together, our data suggest that TIP60-mediated stabilization of ΔNp63α increases cisplatin resistance and has potential implications for cancer treatment and drug design. Additionally, since ΔNp63α confers cisplatin resistance through regulation of genes involved in DNA damage repair, our findings provide critical insight into the mechanism by which genes involved in cisplatin resistance are regulated and may lead to strategies for treating resistant tumors with increased efficacy.
-

Anthrax Event Detection Using Twitter: Analysis of Unigram and Bigrams for Relevant vs Non-Relevant Tweets
Michele Miller and William L. Romine
Due to the lack of anthrax attacks in recent times, researchers have used naturally occurring events to assess their anthrax detection models, but these provide little information on how the models will perform in the context of an unannounced, intentional release of a bioterrorism agent, like anthrax. Therefore, it is important to develop a detection model using data surrounding real anthrax scares and events.We develop a methodology to detect an anthrax-related event on Twitter. We describe a process to separate the tweets concerning anthrax-related events from those not related so experts can address misconceptions and fears in real-time.Most tweets were relevant to Bacillus anthracis. We were able to detect events in real-time and saw a corresponding spike in tweets within 24 hours. Logistic regression performed the best at classifying tweets (F1=0.81). The top used keywords and key phrases for the relevant tweets pertained to anthrax related events while the top keywords and key phrases for the not relevant tweets pertained to the metal band, providing further evidence tweets were classified correctly.This methodology will allow experts to classify tweets concerning anthrax events in real-time to determine misconceptions and address concerns in real-time during future anthrax attacks.
-

Identifying Easy Indicators of Dementia
Swati Padhee, Tanvi Banerjee, Valerie L. Shalin, and Krishnaprasad Thirunarayan
Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) is a degenerative chronic neurodegenerative disease that affects millions of people and whose care costs billions of dollars. There is growing evidence that variations in speech and language may be early indicators of dementia. One of the most initial symptoms of dementia is speech impairment, including difficulty in finding words and changes to the grammatical structure. These early indicators can be detected by having the patients perform a picture description task, such as the Cookie Theft task from the Boston Diagnostic Aphasia Examination. However, much of the state-of-the-art NLP for dementia has been limited due to the size of the available datasets. Understanding the vulnerability of linguistic features extracted from noisy text is essential for both developing better health text classification models and for interpreting the weaknesses of natural language models. This work explores the DementiaBank corpus of Cookie Theft picture descriptions to automatically detect dementia from speech and language translations. Inspired by the results of neuroscience studies, we explore the selective performance of lexical and syntactic features and present quantitative as well as qualitative evaluations.
-

Functional Sites within the IHNV NonVirion Protein that Regulate Host Cellular Responses
Jeff Ringiesn, Bartolomeo Gorgoglione, and Douglas W. Leaman
Fish Rhabdoviruses are responsible for causing fatal epizootics within commercial and wild populations of various fish species around the world. Infectious hematopoietic necrosis virus (IHNV), also known as the Salmonid novirhabdovirus, is enzootic along the Pacific Coast of North America and is comprised of five genogroups, each of which is endemic to a specific geographical location. Once the virus enters the host through the fin epithelia, IHNV infection causes infectious hematopoietic necrosis in salmonid species. The disease is highly fatal and presents with signs such as abdominal distension, bulging of the eyes, anemia, and necrosis of vital organs such as the liver and kidneys, all caused by systemic hemorrhaging within the host.
The 11-kb negative-sense, ssRNA viral genome within IHNV consists of six genes that encode the nucleoprotein (N), phosphoprotein (P), matrix protein (M), glycoprotein (G), nonvirion protein (NV), and RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (L), in order from 3’ to 5’, respectively (Fig. 1). While most of the protein products from the IHNV genome have been studied and elucidated, the precise function of the NV protein remains unknown. While multiple studies have reported various roles for NV, such as suppression of apoptosis, interferon (IFN) induction, and NF-κB activation, data from our lab suggest that NV augments transcriptional or translational responses in the host. Using transient transfections and luciferase reporter assays, we have observed upregulation of host cell transcription/translation and innate immune responses. Regardless of the proposed functions of NV, functional sites within the viral protein are poorly defined. With the introduction of C- and N-terminal deletion mutations (∆NV), we were able to characterize the effects of mutated NV on rainbow trout gill epithelial cell (RT-Gill) constitutive and induced transcriptional responses using specific luciferase reporter plasmids, pCAGluc and RT-IFNluc. Our results suggest that while all ∆NV mutants showed a decrease in the augmented luciferase expression obtained with WT-NV, mutations within the N-terminal region of the protein led to an inhibitory effect on constitutive or induced luciferase expression. These data suggest that the N-terminal region of NV plays a critical role in the upregulation of host cell expression.
-

Predicting alcohol withdrawal in intensive care units
Reza Sadeghi, Tanvi Banerjee, and William L. Romine
Alcohol use disorder is a common health issue in older adults who are facing depression caused by retirement, loss of a spouse, pain, and sleep problems. The prolonged, heavy alcohol ingestion will lead to high alcohol dependency such that cessation or reduction of using alcohol causes alcohol withdrawal syndrome (AWS) in roughly 4 to 72 hours after the last drink. During the initial 8 hours, patients face anxiety, insomnia, nausea, and abdominal pain. This condition is followed by high blood pressure, increased body temperature, unusual heart rate, and confusion. If this syndrome does not receive any treatment, the patients will suffer from hallucinations, fever, seizures, and agitation. As a result, there is an essential need to predict and treat this syndrome in the initial stages. Using physiological signals, we examined the predictability of AWS over the records of patients who stayed in critical care units in Medical Information Mart for intensive care III (MIMIC-III). This dataset contains the records of 243 patients who were admitted in ICUs with the primary issue of AWS. 65% of all the patients diagnosed with mental illness as primary health concern suffered from AWS. To have a fair comparison, an equal number of records of patients without AWS are considered as the control group. We extracted nine descriptive statistical features from physiological signals and medical history of patients: average heart rate, average amount of magnesium in the blood, average body temperature, average systolic blood pressure, maximum systolic blood pressure, minimum systolic blood pressure, age, gender, and length of stay in intensive care units. The computed features were fed into 11 supervised machine learning classifiers to identify AWS conditions. The outcomes demonstrate that the Naïve Bayes classifier with an accuracy of 0.85 outperformed the others in detecting patients with AWS. This finding can help critical care physicians identify potential AWS in earlier stages and provide potential interventions before the symptoms reach a detrimental level.
-
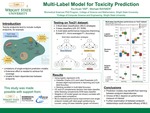
Multi-Label Model for Toxicity Prediction
Xiu Huan Yap and Michael L. Raymer
Most computational predictive models are specifically trained for a single toxicity endpoint. Since more than 1300 toxicity assays have been reported in the TOXCAST dashboard, achieving high coverage over this growing number of toxicity endpoints remains challenging. Furthermore, single-endpoint models lack the ability to learn dependencies between endpoints, such as those targeting similar biological pathways, which may be used to boost model performance. In this study, we characterize the performance of 3 multi-label classification (MLC) models, namely Classifier Chains (CC), Label Powersets (LP) and Stacking (SBR), on Tox21 challenge data. These MLC models employ the Problem Transformation approach, which is algorithm-independent and thus generally compatible with existing classifiers. Using Logistic Regression as the base classifier and random label partitioning (k=3), CC and LP show statistically significant improvement in model performance using Hamming and subset 0/1 scores (p
-

Wright State University's Symposium of Student Research, Scholarship & Creative Activities from Friday April 13, 2018
Wright State University
The student abstract booklet is a compilation of abstracts from students' oral and poster presentations at Wright State University's Symposium of Student Research, Scholarship & Creative Activities on April 13, 2018.
-

Measuring Gender-Based Violence Attitude on Twitter
Goonmeet Bajaj, Tanvi Banerjee, Amir Hossein Yazdavar, Valerie L. Shalin, and Amit Sheth
This study examines social media to analyze communication patterns, specifically in the Gender-Based Violence domain. It explores the pragmatic content of tweets to categorize them into one of the following groups: Belief, Fact Reporting, or Other to determine the tweeting practices prevalent in this domain.
-

Legalization of Gay Marriage and its Impact on Military Stereotypes of Homosexuals
Jasmine Moore
Homosexuality has become a popular research topic in a variety of professional fields, and over the last decade has become a priority for the military. Since the implementation of the law repealing Don't Ask Don't Tell (DADT) researchers have questioned what effects repealing this law has had on the military as a whole. Particular attention has been spent on studying the attitudes and stereotypes about homosexuals after DADT was repealed. However, there is a lack of research examining how marriage equality affects society's stereotypes about homosexuals serving in the United States military.
It was hypothesized that participants that have personal contact (friends or family members) with lesbian, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) individuals will be less likely to hold negative stereotypes about LGBT serving in the armed forces than those participants who don't have personal contact (friends or family members) with LGBT individuals. The purpose of this research is threefold: 1) reduce discrimination of homosexuals serving in the military 2) help to improve the quality of life for homosexuals serving in the armed forces and 3) improve society by increasing tolerance. Current literature does not provide us with a clear and concise picture of how marriage equality impacts military stereotypes of homosexuals. This study utilized survey-sampling methods in an attempt to understand how opinions about marriage equality affect military stereotypes of gays and lesbians. The results supported the main hypothesis. Participants who had personal contact (friends or family members) with LGBT individuals were in fact less likely to hold negative stereotypes about LGBT serving in the armed forces than those participants who did not have personal contact (friends or family members) with LGBT individuals. One can conclude that marriage equality has helped to reduce society's negative stereotypes about homosexuals serving in the U.S. military.
-

Treating Chronic Post Herpetic Neuralgia Using Topical Superconcentrated Capsaicin
Jaree Naqvi, Scott Seider, Jason Miller, Cole Budinsky, and Amol Soin
Post Herpetic Neuralgia (PHN) is a painful condition that occurs after reactivation of the dormant Herpes Zoster Virus.Typically PHN presents with a unilateral rash affecting a single dermatome which is accompanied by burning, irritation, and hypersensitivity for >3 months.Current treatment includes anticonvulsants, tricyclic antidepressants, narcotic/nonnarcotic painkillers, and topical lidocaine.
We propose the utilization of a superconcentrated transdermal patch of capsaicin called Qutenza 8%, which is 300 times more potent than current OTC capsaicin. The treatment protocol using Qutenza to treat refractory PHN proposes a novel approach to the treatment of this condition.
Capsaicin is commonly known as the active chemical in peppers which is responsible for their spiciness and the pain and irritation associated with ingesting them. The mechanism of action of capsaicin is believed to be release of neurotransmitters upon binding to capsaicin nociceptors, mainly TRPV1. At large doses, capsaicin causes depletion of neurotransmitters and can ultimately lead to nerve fiber denervation. Once the neuron is damaged or depleted of neurotransmitters, pain perception is notably diminished for a period of time thereby effectively providing relief
-

kHealth Bariatrics: A Multisensory approach to monitoring Patient’s Postsurgical Behavior
Revathy Venkataramanan, Utkarshani Jaimini, Amit Sheth, Joon K. Shim, Priti Parikh, and Dene S. Berman
The rate of obesity is on the rise reaching epidemic proportions. According to American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (ASMBS), 500 million people all over the world are obese. The data from Centers for Disease Control and Prevention(CDC) shows that more than 36% of adults in the United States have obesity. According to World Health Organization (WHO), 65% of the world’s population lives in countries where the occurrence of death due to overweight and obesity is higher than being underweight. It is well established that weight loss surgery can play a significant role in reducing, or even eliminating medical problems associated with obesity. Weight recidivism is one of the biggest challenges following bariatric surgery. As many as 50% of patients may regain a small amount of weight two years or more following their bariatric surgery. A lifetime commitment to diet and behavior modifications after surgery are essential for success after undergoing surgery.
In this project, computer scientists working at Kno.e.sis, an Ohio Center of Excellence in BioHealth Innovation, are collaborating with a bariatric surgeon and a psychologist to bolster weight loss surgery patients for appropriate postsurgical progress. In our mobile personalized digital health solution, we use an Android application coupled with sensors to monitor patient’s compliance with post-surgery progress and motivate patients to have proper follow-ups. The sensors include a wireless weighing machine that automatically sends data to the cloud, activity and sleep monitoring wristband which also measures heart rate, water bottle sensor and pill bottle sensor which prompts the patient for proper intake of water and vitamin pills. Additionally, the android app with its simple questionnaire helps in monitoring the patient’s diet and emotional well-being.
One of the key challenges for the surgeon is to continuously monitor the patient to identify the deviations from recommended postsurgical guidelines. We aid bariatric surgeons to identify noncompliance with direction by providing aggregated data of all the primary parameters to be monitored. We also monitor patient’s mental health, following diet and sleep cycle. Thus, a joint effort with the surgeon and psychologist to track patient’s postsurgical behavior differentiates our approach from others and contributes to improved outcomes for bariatric surgery patients.
-

Social Workers’ Salaries vs. Educational Student Debt Burden: A Losing Battle
Michael Wadham
College tuitions rise at disparate rates with starting salaries and inflation, causing student debt to weigh on social work graduates. Data was collected from 701 social workers in an NASW - Ohio Chapter survey to investigate this disparity and its consequences. The purpose of this study was to analyze the qualitative data set, 174 written comments, for themes and perceptions. The following themes, echoed in current research on the topics of social work salary and student debt burden, were identified: unmanageable debt and financial burden, varying lengths of time and repayment methods, social workers feeling undervalued and underpaid, loan forgiveness programs, and the need for greater advocacy for social workers’ educational debt relief. The demand for social work is projected to grow; this research is important to help maintain the needed workforce so social workers do not leave the profession to pursue a living wage, or choose another path entirely.
-

Wright State University's Celebration of Research, Scholarship and Creative Activities Book of Abstracts from Friday, April 21, 2017
Wright State University
The student abstract booklet is a compilation of abstracts from students' oral and poster presentations at Wright State University's Annual Celebration of Research, Scholarship and Creative Activities on April 21, 2017.


